- sales@bminfotradegroup.com
- 53-A, Vishnupuri, Dalda Factory Road, Durgapura, Jaipur -302018

CCTV stands for closed-circuit television and is commonly known as video surveillance. “Closed-circuit” means broadcasts are usually transmitted to a limited (closed) number of monitors, unlike “regular” TV, which is broadcast to the public at large. CCTV networks are commonly used to detect and deter criminal activities and record traffic infractions, but they have other uses.
CCTV technology was first developed in 1942 by German scientists to monitor the launch of V2 rockets. It was later used by American scientists during the testing of the atomic bomb.


CCTV surveillance can deter potential criminals. When a crime does occur, video footage can help law enforcement to investigate and later provide evidence for the prosecution in a law court. Used in conjunction with CCTV, audio, thermal and other types of sensors can alert officials to occurrences that are out of the ordinary, e.g. fire or gunshots at a location. For businesses, CCTV cameras can detect and monitor in-house criminal activities. Prisons may use video surveillance to prevent drones from delivering drugs and other contraband to prisoners. Cameras are able to monitor areas that are not easily accessible, e.g. rooftops.
Using CCTV cameras, emergency services and rescue workers are able to assess and monitor events in real-time to relay a “situation” via video to disaster management teams, e.g. from inside a burning building, from a cave, or from a helicopter flying over a scene.
Cameras at traffic lights and elsewhere in cities monitor people to gather traffic statistics as well as evidentiary footage for speeding. An heir to the IoT, the IoT is a Chicago initiative to collect real-time data, primarily weather and environment, about the city. Some sensory nodes include cameras that analyze the images they record but, in order to protect individuals’ privacy, do not transmit or store these images. In the main, a limited number are stored for use by senior researchers in order to “develop the computer vision software”. The project has met with some resistance from privacy watchdogs.
CCTV used to research suicide found that 83 percent of people attempting to throw themselves in front of a train showed specific behaviors. These were later analyzed from CCTV footage and are now used to alert monitor watchers to potential suicides. Surveillance networks are also used by researchers to record crowd activities in public places and prevent anti-social behaviors. For instance, cameras have been used at schools for security, and to record bullying or playground incidents.
CCTV used to research suicide found that 83 percent of people attempting to throw themselves in front of a train showed specific behaviors. These were later analyzed from CCTV footage and are now used to alert monitor watchers to potential suicides. Surveillance networks are also used by researchers to record crowd activities in public places and prevent anti-social behaviors. For instance, cameras have been used at schools for security, and to record bullying or playground incidents.
Market intelligence garnered from video surveillance of customers is being used to analyze buying trends and enable enhanced strategizing, e.g. how do people shop, which aisles do they traverse the most, how likely are they to respond to calls to action within different store layouts? Heat maps can show the highs and lows of shopper traffic at specific locations in a store, helping stores to identify peak buying times, preferred promotion types, and staffing requirements for peak shopping periods.
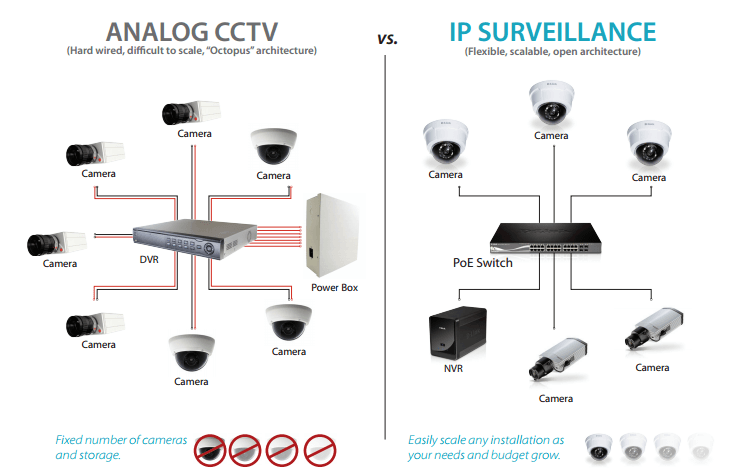
Analog and digital systems work quite differently but modern CCTV networks use conversion software and hardware to convert analog to digital.
This process is called retrofitting.
A traditional CCTV system comprises:


Copyright © 2021 BM INFOTRADE PVT LTD. Designed By Unitech IT Solution