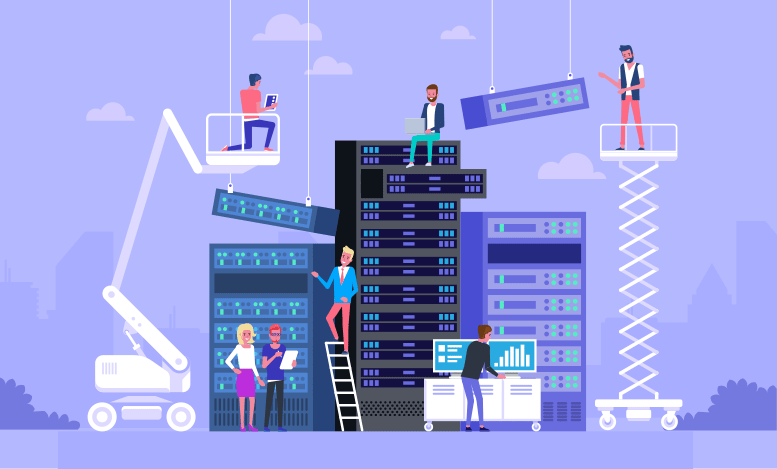
SAN: Storage Area Network
Storage area networks (SANs) are the most common storage networking architecture used by enterprises for business-critical applications that need to deliver high throughput and low latency. A rapidly growing portion of SAN deployments leverages all-flash storage to gain its high performance, consistent low latency, and lower total cost when compared to spinning disk. By storing data in centralized shared storage, SANs enable organizations to apply consistent methodologies and tools for security, data protection, and disaster recovery.
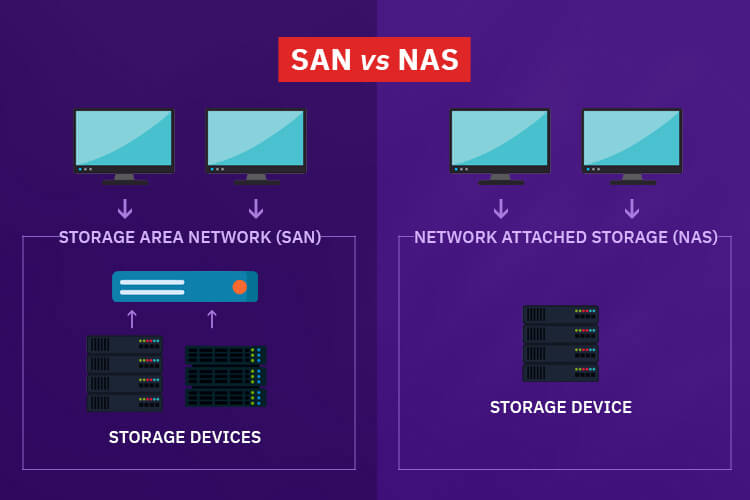
A SAN is a block-based storage, leveraging a high-speed architecture that connects servers to their logical disk units (LUNs). A LUN is a range of blocks provisioned from a pool of shared storage and presented to the server as a logical disk. The server partitions and formats those blocks—typically with a file system—so that it can store data on the LUN just as it would on local disk storage.
Advantages Of SAN:
SANs make up about two-thirds of the total networked storage market. They are designed to remove single points of failure, making SANs highly available and resilient. A well-designed SAN can easily withstand multiple components or device failures.
NAS
A storage server is a type of server that is used to store, access, secure, and manages digital data, files, and services. It is a purpose-built server used for storing and accessing small to large amounts of data over a shared network or through the Internet. A storage server may also be called a file server. A storage server is typically less powerful than a standard server, but has more storage space, storage access interfaces, and specialized data retrieval and management utilities. A storage server generally serves as a central point of access for data storage and access. Local client nodes and remote computers access the storage server through a GUI control panel and FTP or programmatic API access by software and applications. It can be used for routine or frequently used data storage and access, or it can serve as a backup server for storing backup data.
A storage server is an integral part of direct-attached storage (DAS), network-attached storage (NAS), and other storage networking technologies.
Advantages of having a storage server
In the past, most small companies didn’t use file servers because of their high cost of installation. Instead, they chose to store all important documents on one desktop. The main disadvantage of this practice was that every time an important document was required, only that desktop was to be accessed (you can imagine the inconvenience). The main benefit of the file server is the space it provides to store files which is available to all computers attached to a network. It is useful when many need access to the same file (removing the need to make multiple copies). Files can be monitored because they are all stored at a single location. File servers enable better data management while providing extra security (information stored can be password protected).